|
|
This low impedance works to isolate the inputs by forming a voltage divider with the 10k input resistors. Because the cathode rest a few volts above ground, the 40µF coupling capacitor is needed to protect the input sources from the DC offset. An alternative topology is one with a coupling capacitor per input resistor. While these coupling capacitor would be smaller in value than the single capacitor, it is a nuisance to have any coupling capacitors. Eliminating these coupling capacitors requires giving the grid a counter bias voltage sufficient to bring the cathode to ground level. And the power supply noise can lessened by the same partial cathode resistor bypass trick as used in the last circuit.
Further hotrodding of the this circuit entails replacing the cathode resistor with a current source. The current source subtlety improves the mixer's performance. The actual effective impedance of the current source is equal to the rp added to the cathode resistor against the mu plus 1. In this example, 343k is the effective value.
|
|
|
|
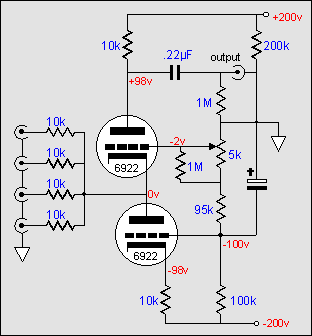
Some readers might be having a hard time understanding how this circuit works. The key is to think current and not voltage. A +1 volt pulse at the input of one of the 10k resistors leads to a .1 mA pulse at the top triode's cathode. Now the question is where will the current pulse go? The current source is maintaining a constant current draw so it cannot easily up its conduction. This leaves the top triode to give up .1 mA less conduction. And as the plate resistor is in series with the triode, its voltage drop must decrease by .1 mA against its 10k value. In other words, the top triode's plate sees a +1 volt pulse. In contrast, a negative going 1 volt pulse at the input will force the top triode to increase its conduction by .1 mA and thus pull its plate down by one volt.
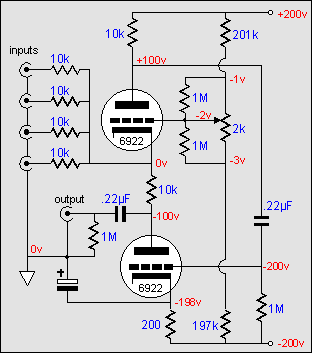
A further modification of this circuit is to apply a White-cathode-follower like topology to the circuit. Shown below is the result. The output is taken at the bottom of the center 10k resistor and is consequently phase inverted. The .22µF capacitor supplies a feedback path from the plate of the top triode. The feedback works to lower the impedance at the top triode's cathode by utilizes the transconductance of both the tubes. The potential danger to this circuit is the large voltage potential between the two cathodes. This requires using two separate tube envelopes and two floating heater power supplies.
|
|